1、打开一个文件open()
handle=open(filename,mode)
mode为文件打开的模式,‘r’表示只读,’w’表示可写,‘rb’表示二进制只读格式,’wb’表示二进制可写格式,默认是只读模式。
open()函数返回一个file handle(文件句柄),可以将之视为一系列的行。
handle=open('temp.txt')#返回文件句柄
for i in handle:
print(i)
输出:
this is first line
this is second line
this is third line
上述输出结果中,每一行之间出现空行,是因为print()在执行时,在行与行之间多了一个执行‘\n’换行符的操作。可以使用strip()来避免这种情况出现。
handle=open('temp.txt')
for i in handle:
print(i.strip())
输出:
this is first line
this is second line
this is third line
2、读取一个文件read()
对open()函数返回的file handle(文件句柄)执行读取操作,能够读取的前提条件是open()的mode是‘r’(只读)而不是’w’(可写)。
file=open('temp.txt')
print(file.read())
输出:
this is first line
this is second line
this is third line
3、文件写入write()
对open()函数返回的file handle(文件句柄)执行写入操作,能够写入的前提条件是open()的mode是’w’(可写)而不是‘r’(只读)。如果原文件中有内容,write()默认擦除原文件中的内容再执行写入操作。
#对一个空文件执行写入操作
handle=open('temp.txt','w')#以可写模式打开文件
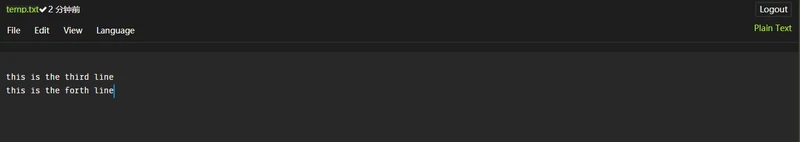
handle.write('\nthis is the third line')
handle.write('\nthis is the forth line')
handle.close()#close()在这里相当于’save'操作
写入后的文件如下图所示:
#将from_file文件中的内容写入到to_file文件中
handle=open('to_file.txt','w')
handle.write(open('from_file.txt').read())
handle.close()
4、文件清空truncate()
对open()函数返回的file handle(文件句柄)执行文件清空操作,能够清空的前提条件是open()的mode是’w’(可写)而不是‘r’(只读)。该命令要谨慎使用!
handle=open('temp.txt','w')
handle.truncate()
handle.close()
5、移动文件读取指针到指定位置seek()
对open()函数返回的file handle(文件句柄)执行指针移动操作
seek(offset[, whence])
offset:需要移动偏移的字节数
whence:可选,默认为0,代表从文件头开始偏移;1代表从当前位置开始偏移;2代表从文件末尾开始偏移。
seek(0)命令在很多文件处理中必不可少,因为如果已经执行完read()后,文件的读取指针已经在文件的末尾。接下来继续执行read()或者readline(),如果不将读取指针重置到文件开头,read()或者readline()读取出来的内容都是空。
handle=open('temp.txt')
handle.read()
输出:‘this is test\n2 test\n3 test’
handle.seek(0)
handle.readline()
输出:‘this is test\n’
6、读取文件中的一行readline()
对open()函数返回的file handle(文件句柄)执行行读取操作,这里每次执行完后,文件的读取指针后移一行,多次执行该命令,可以按行读取文件。
